ConnectingGasCylinders
Gas chromatography requires the use of
a carrier gas to carry a sample from the
injection port to the column and onto the
detector. Depending on the type of de-
tector, other gasesmay be required. The
FID detector for instance, requires hy-
drogen and air to support the flame. This
document will discuss how carrier and
detector gases are connected to the gas
chromatograph and how to properly
manage gas cylinders.
Gas cylinders should
always
be safely
and properly secured to the wall through
the use of straps, chains or other secur-
ing devices. Cylinder straps are availa-
ble from the companywhich supplies the
gas cylinders.
Carrier/detector gases can be either
flammable or non
-
flammable. Hydrogen
and argon/methane are commonly used
flammable gases while helium, argon,
and nitrogen are common non
-
flammable gases.
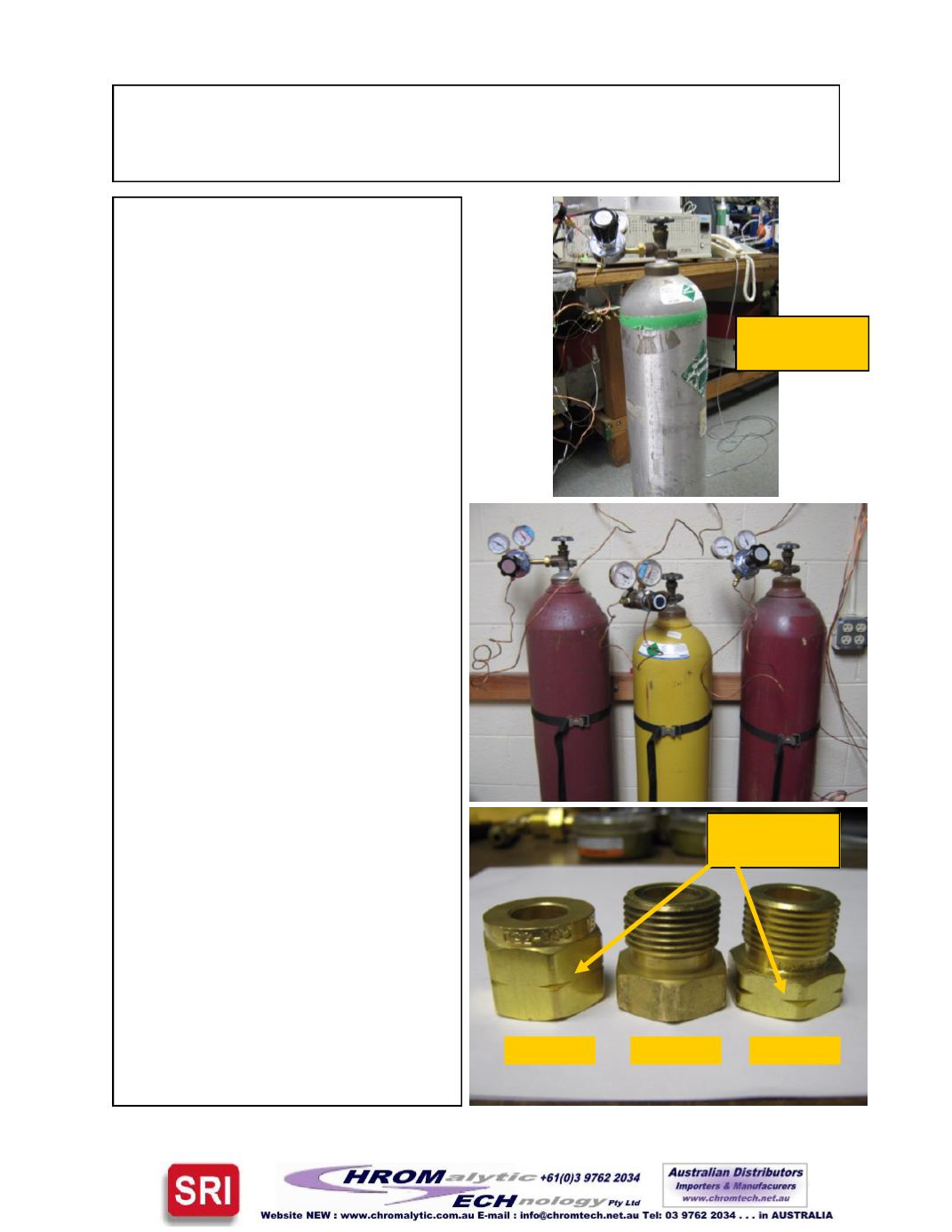
Different nuts are used to connect the
gas cylinder regulator to the different
gases. CGA stands for Compressed
GasAssociation.
1) CGA
-
350 is used for hydrogen and
argon/methane.
2) CGA
-
580 is for helium, nitrogen or
argon.
3) CGA
-
590 is for air.
Notice that the CGA 350 and 590 nuts
have a gash in the nuts. This indicates
that the nuts tighten up in the reverse
direction from normal (counter
-
clockwise
instead of clockwise).
Page1
CGA-350
CGA-580
CGA-590
Typical gas
cylinder
Gash innut


