pharmaceutical
Applications
note
RestekCorporation • (800)356-1688 • (814)353-1300 •
#59151
pharmaceutical
Analyzing Cardiac Medications by HPLC
In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading
cause of death. In an effort to reduce mortality from heart
disease, several classes of medications are used to decrease
high blood pressure, control arrhythmias (abnormal heart
rhythms), and treat congestive heart failure. Many of these
cardiac medications include beta antagonists, ACE inhibi-
tors, diuretics, or calcium channel blockers.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is the
preferred technique to analyze many of the compounds used
in these medications. To maximize the effectiveness of the
separation, a chromatographer should choose the column
and conditions that best allow amplification of structural
differences between matrix components, related compounds,
and analytes. Proper HPLC column selection is dictated by
the analyte and the sample matrix. In fact, selecting the
appropriate analytical column is critical when analyzing
cardiac medications because many of them contain basic
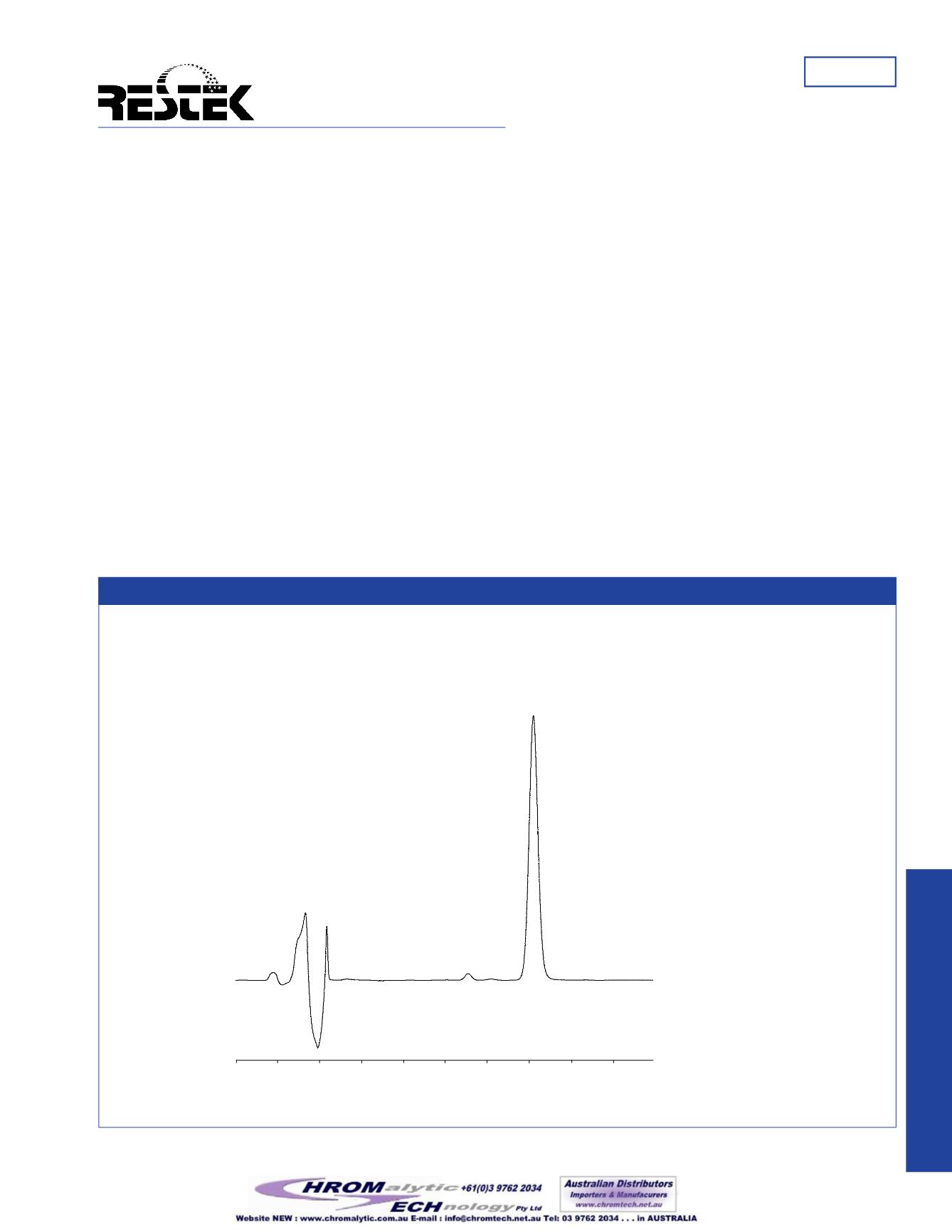
Figure1
Ultra IBD column provides alternate selectivity, which separates impurities in a digoxin standard.
compounds, which tend to tail badly on poorly deactivated
HPLC phases. Restek’s fully end-capped Allure
™
Basix, Ultra
IBD (intrinsically base deactivated), and Ultra Cyano phases
can use the basic nature of these compounds to achieve a
separation that will not suffer from the problems normally
resulting in peak tailing.
AngiotensinConvertingEnzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
Ancient Egyptians used the ACE inhibitor, digoxin, as a
poison. Ancient Romans used it as a wound dressing and
heart stimulant. It is extracted primarily from the poisonous
foxglove plant in a concentration of up to 0.4% by mass. A
commercial digoxin standard claiming 100% purity is shown
to be impure when the analysis is performed using the Ultra
IBD column. The alternate selectivity of this phase to alkyl
stationary phases results in the separation of two unknown
impurity peaks in the digoxin standard (Figure 1).
LC_0068
Column:
Ultra IBD
Catalog #:
9175565
Dimensions:
150 x 4.6mm
Particle Size:
5µm
Pore Size:
100Å
Conditions:
Mobile phase:
water with 0.1% (v/v)
acetic acid:acetonitrile
(65:35, v/v)
Flow:
1.0mL/min.
Temp.:
27°C
Det.:
UV @ 220nm
Peak List:
1. unknown
2. unknown
3. digoxin
Sample:
Inj.:
10µL
Conc.:
1000µg/mL
Solvent:
water:methanol (1:1, v/v)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 min.
1 2
3


