environmental
Applications
note
Restek Corporation • (800) 356-1688 • (814) 353-1300 •
#59359
ImprovedAnalysisof OrganophosphorusPesticidesUsingRtx
®
-OPPesticides
andRtx
®
-OPPesticides2Columns
environmental
Organophosphorus pesticides (OPPs) are an important group of
insect control agents used in agricultural and home settings.
Although there are continuing concerns about their effects on
health, their relatively low toxicity and short environmental fate
havemade them suitable replacements for banned organochlorine
pesticides, especially in agricultural applications. Because of their
widespread use, it is necessary to routinelymonitor treated foods
and surrounding soils and groundwater after OPPapplication, to
ensure low residue levels.
Historically, the analysis of OPPs has presented challenges. US
Environmental ProtectionAgency (EPA)Methods 8141 and
8141Awere developed to help laboratories analyze soils, water,
and solidwastes for OPPs.Method 8141Adescribes themany
problems that can occur during capillaryGC analysis. TheOPP
compounds represent a diverse group, many of which are photo-
sensitive or easily degraded during routine standard preparation,
storage, and analysis. In addition, individual analytes can be diffi-
cult to identify because of the large number of OPPs that might be
present (e.g., a total of 49 possible analytes are listed inMethod
8141A), and in the past GC/MS has not been sufficiently sensitive
for routine use. Consequently, ion-specific detectors (e.g., a nitro-
gen phosphorus detector [NPD] or flame photometric detector
[FPD] in the phosphorusmode)must be used to ensure sensitivity
to detect low ppb levels of OPPcompounds. This requires dual-
column analysis for confirmation of analyte identities. Even the
current EPAmethod states, it is unlikely that all of them [OPPs]
could be determined in a single analysis.
1
Many capillary phases have been used for this dual-column analy-
sis, but most present a large number of coelutions that make posi-
tive identifications difficult. For example, there are seven known
pairs of coelutions on the 5% phenyl analytical column named in
Method 8141A, and nine pairs of coelutions on the confirmation
column. Until now, theRtx
®
-OPPesticides column has given the
best resolution of organophosphorus pesticides in the shortest time
(Figure 1).
TheRtx
®
-OPPesticides column has advantages over other current
technologies, but until now there has not been a confirmation col-
umn that has as few coelutions in as short an analysis time, to
make it compatiblewith theRtx
®
-OPPesticides column. To provide
a good confirmation column tomatch theRtx
®
-OPPesticides col-
umn, Restek chemists have developed a new polymer phase, the
Rtx
®
-OPPesticides2 phase. In combination, these two columnswill
reduce the number of chromatographic coelutions and provide sep-
arations in less than 25minutes.
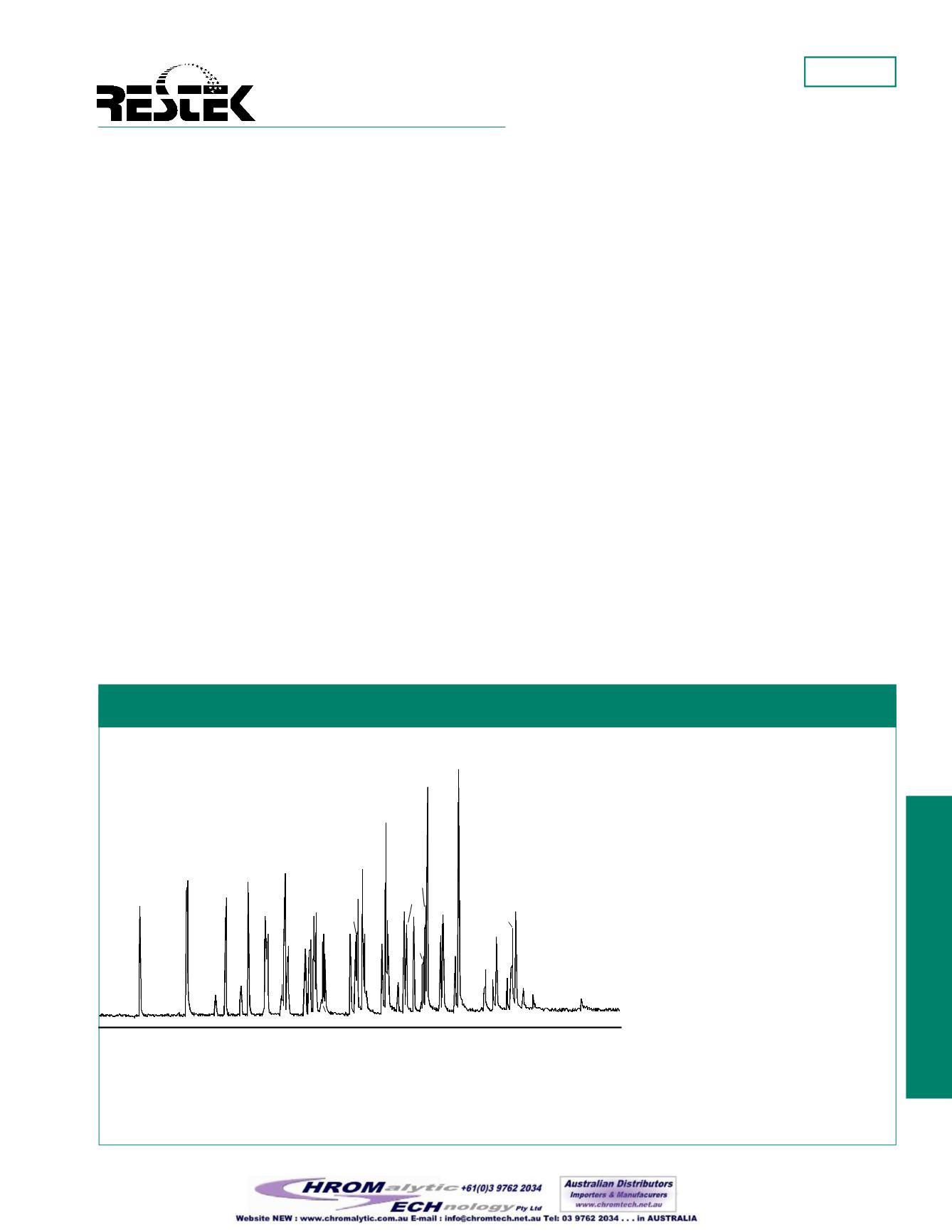
Figure 1—
TheRtx
®
-OPPesticides columnprovides good resolution and short analysis time for
organophosphorus pesticides.
Column:
Rtx
®
-OPPesticides 30m, 0.32mm ID, 0.50µm (cat.# 11239)
Sample:
1.0µL of customOP pesticidesmix described in Figure 3 (GC_EV00602)
Concentration:
100ppb
Inj.:
direct injection, Uniliner
®
DI liner (cat.# 20335)
Oven temp.:
100°C to 180°C@ 10°C/min. (hold 2min.), to 300°C@ 18°C/min. (hold 2min.)
Inj. &Det. temp.:
250°C
Detector:
FPD
Flow rate:
5cc/min., helium
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 12
13
14 15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22,23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
36,37,38
39
40
41
42,43
44
45
46
47
48,49
50
51
52
53
1. dichlorvos
2. hexamethylphosphoramide
3. trichlofon
4. mevinphos
5. demeton-S
6. zinophos
7. ethoprop
8. phorate
9. naled
10. sulfotepp
11. tributylphosphate (IS)
12. diazinon
13. terbufos
14. fonofos
15. TEPP
16. dioxathion
17. disulfoton
18. demeton-O
19. dichlorofenthion
20. chlorpyrifosmethyl
21. dimethoate
22. dicrotophos
23. monocrotophos
24. ronnel
25. merphos
26. chlorpyrifos
27. aspon
28. fenthion
29. trichloronate
30. phosphamidon isomer
(breakdown product)
31. methyl parathion
32. malathion
33. fenitrothion
34. tokuthion
35. phosphamidon
36. chlorfenvinphos
37. parathion
38. merphos oxone (merphos
breakdown product)
39. stirophos
40. crotoxyphos
41. bolstar
42. carbophenthion
43. ethion
44. triphenylphosphate (IS)
45. leptophos
46. fensulfothion
47. tri-
o
-cresyl phosphate
48. phosmet
49. EPN
50. famfur
51. azinphosmethyl
52. azinphos ethyl
53. coumaphos
35
GC_EV00631


