RestekCorporation
(800) 356-1688
ClinicalForensic
BarbiturateAnalysis
note
A
pplications
cat.#59575
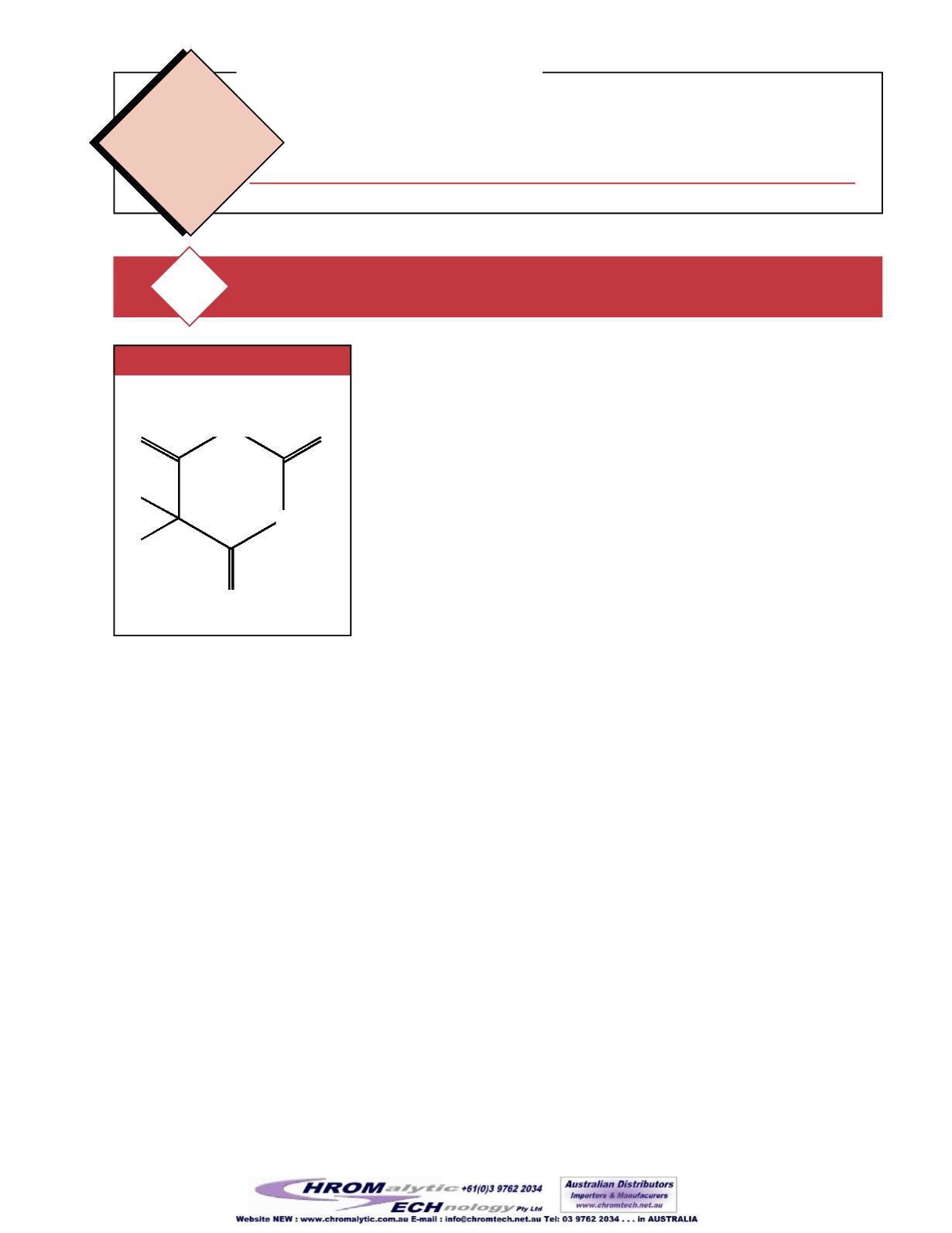
Figure 1
BasicStructure forBarbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of compounds
that are central nervous system
depressants. They are categorized as
sedatives or hypnotics and areprimarily
used in the treatment of anxiety,
insomnia, andconvulsivedisorders.
Physical effects of thebarbiturates
range frommild sedation to coma.
Barbiturates arebasedon apyrimidine
ring structure. Substitution at the 2, 4,
and6positions gives the basic structure
for theoxybarbiturates (
Figure1
).
Replacement of theoxygen at position2
with sulfur results in the formationof
thiobarbiturates.Barbiturates canbe
ranked according to their onset of
activity, durationof action anddegree
of hypnoticpotency. Thesepharmaco-
logical effects are influencedby the
types of functional groups attached at
position5. The inclusionof alkyl or aryl
groups, thenumber of carbons in the
alkyl side chains, and the degree of
branchingwill affect activity and
toxicity.
Extended administrationor abuseof
barbiturates can lead tophysical and
psychological dependence. Tolerance to
the effects of barbiturates on the central
nervous system canbe built upwith
continued exposure to thedrug.While
tolerance to the intoxicating effects of
barbituratesmay increasewithuse,
there is very little increase in tolerance
to the toxic side effects of highdoses.
As a result, the therapeutic index for
barbiturates is lower than for other
sedative/hypnoticdrugs like the
benzodiazepines. Thebarbiturates also
have an additive effectwhen adminis-
teredwithother central nervous system
depressants. The combinationof the
low therapeutic index and the additive
effects of otherCNSdepressantsmakes
monitoring for barbiturates an important
aspect of drugoverdose screening.
Barbiturates canbe analyzed in either
their underivatizedor derivatized forms
bygas chromatography.Derivatization
of thebarbiturates ismost commonly
performedbymethylationof the amido
nitrogens inpositions 1 and3.Methy-
lating reagents like tetramethylammo-
niumhydroxide (TMAH) and trimethyl-
aniliniumhydroxide (TMPAH) canbe
used for on-columnderivatizationof the
barbiturates.While
derivatization can improve thepeak
shape and response, extraneous peak
formation can interferewith some
analyses. Proper injectionport set-up is
important inobtaining reproducible
resultswithon-columnderivatization.
Methylationof barbiturates is catalyzed
by the additionof heat to the reaction
mixture.After sample injection, the
residence timeof thebarbiturates and
thederivatizing reagent inside the
injectionport is very short. Since
contact of the samplewith the heated
surface area inside the injectionport
liner needs tobemaximized, liners that
are packedwithwool or that contain
flowdisrupting elements, like the
Cyclosplitter
®
sleeves are recom-
mended. In addition, injectionport
temperatures shouldbemaintained in
O
NH
1
2
3
4
5
6
NH
O
O
R
1
R
2


