pharmaceutical
Applications
note
RestekCorporation • (800)356-1688 • (814)353-1300 •
#59133
pharmaceutical
1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8min.
2 3
4
Excellent LC/MS Separation of Penicillins and Cephalosporins Using
Ultra IBD Columns
Antibiotics are the most widely used medications in the
world. Whether by prescription, addition to animal feed
stocks, or use of cleaning agents, everyone in the civilized
world is either directly or indirectly exposed to antibiotics
in daily life. The overuse of antibiotics, however, has
allowed resistant bacteria to thrive. The death of 12,500
people in Guatemala from an episode of Shingella fever can
be traced to a simple mutation of the bacterial strain.
Research indicated that the bacterium incorporated a single
plasmid into its RNA sequence and resultantly became
resistant to four different antibiotics. This illustrates the
danger of resistance caused by adaptation. To combat
resistant bacteria, new antibiotic derivatives must be created
to overcome the bacteria’s new defense mechanisms.
Typically, HPLC columns can be used to analyze penicillins
and their structurally related cephalosporins. However, the
similarity of many derivatives may require additional
interactions to effectively separate related compounds.
Restek’s Ultra IBD column is better able to resolve these
compounds using polar and hydrophobic interactions.
Background
Penicillins and cephalosporins represent nearly sixty percent
of antibiotics worldwide. These antibiotics possess a sulfur
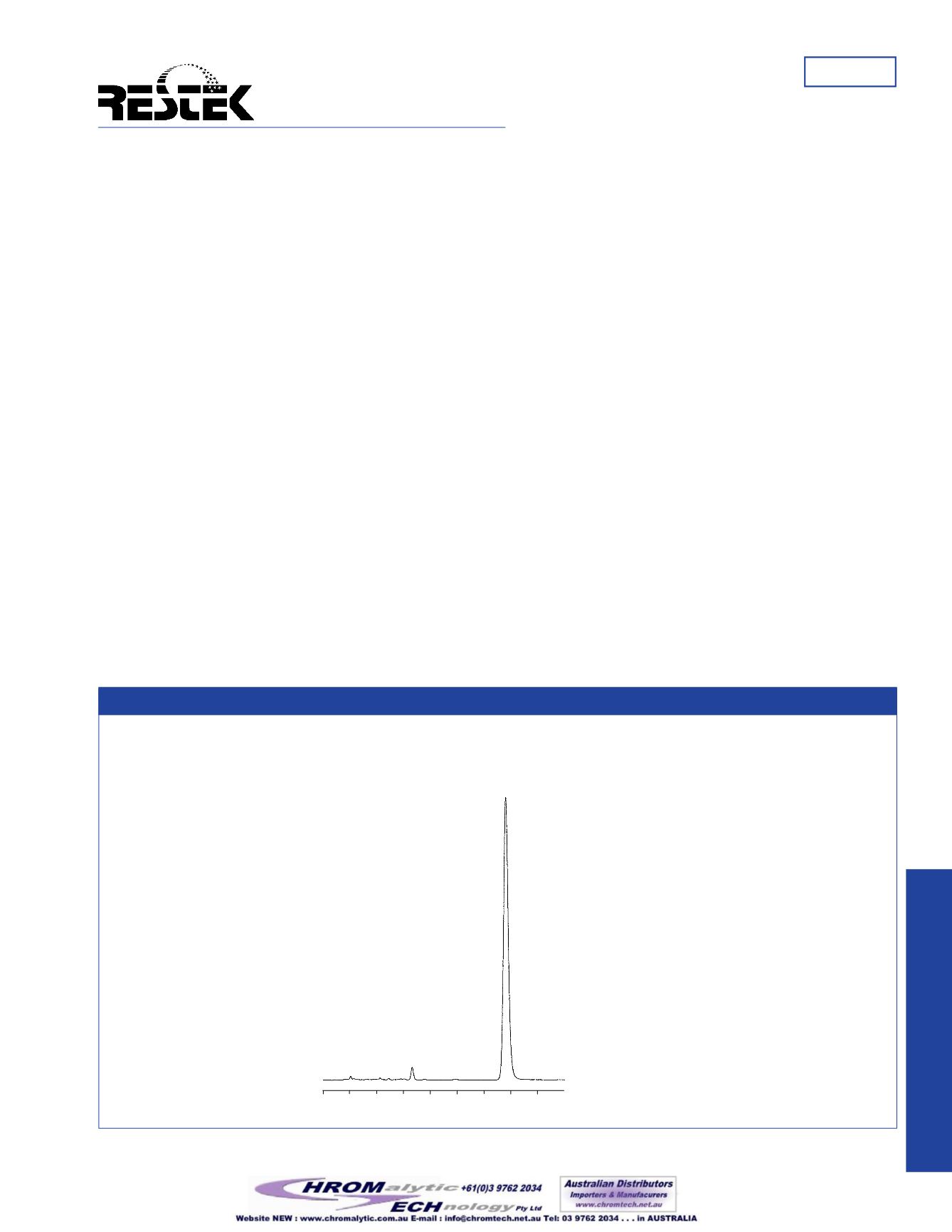
Figure1
Ultra IBD separates penicillinV from other fermentation impurities.
LC_0096
atom within a five- or six-membered ring, attached to a four-
member ß-lactam ring. They are produced by fermentation
processes using either selected fungi or species of
Strepto-
myces
bacteria. Derivatives are produced in two fashions:
1.
Biosynthetic process—The fungus or bacteria are
genetically engineered to produce a new derivative, or the
starting materials are altered to produce biosynthetic
variants during fermentation.
2.
Semi-synthetic processes—The materials from a biosyn-
thetic process are converted to chemical derivatives.
Penicillin derivatives are created from penicillin G or V,
while cephalosporin derivatives are created from cepha-
losporin C or cephamycin C.
Unfortunately, biosynthetic fermentation does not produce
a “pure” antibiotic. Even after cleanup of the fermentation
mash, some side reaction products will remain. Many of
these side products are closely related to the primary analyte
(Figure 1). Desired products, however, are created in the
semi-synthetic process. Penicillin V is converted to
amoxicillin through chemical intermediates and varies only
slightly in structure (Figure 2). Similar reactions also occur
during production of cephalosporin derivatives. The loss of
Peak List:
1. unknown
2. unknown
3. unknown
4. penicillin V
Sample:
Inj.:
2.5µL
Conc.:
1.2mg/mL
Solvent: acetonitrile:water (10:90, v/v)
Column:
Ultra IBD
Catalog #:
9175565
Dimensions:
150 x 4.6mm
Particle Size:
5µm
Pore Size:
100Å
Conditions:
Mobile Phase:
10mM ammonium
formate, pH 2.5:
acetonitrile (60:40, v/v)
Flow:
1.2mL/min.
Temp.:
30°C
Det.:
UV @ 270nm


