• 6 •
www.restekcorp.comMTBE & Oxygenate Analysis
Using an Rtx
®
-VGC GC Column
Gasoline and other fossil fuels are derived from
petroleum and consist mainly of compounds con-
taining only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Oxygenates are compounds that contain oxygen
atoms in addition to carbon and hydrogen. Methyl
tert
-butyl ether (MTBE) is the most common fuel
oxygenate. MTBE was first introduced into gasoline
in 1979 to reduce overall emissions, replace lead
and increase octane. In 1992, gasoline with up to
15% MTBE content by volume was used nationally
to meet the first federally mandated wintertime
reduction of carbon monoxide. With over one mil-
lion underground fuel tanks in the United States
alone, contamination of ground and surface water
with oxygenates and gasoline components is a
major environmental concern. Potentially, storage
tanks worldwide will require cleanup. An equally
challenging task is the identification and quantita-
tion of these fuel-derived pollutants.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has
not sanctioned any method specifically for the
analysis of oxygenates in gasoline. However, envi-
ronmental laboratories have used a variety of meth-
ods to report these analytes, such as US EPA
Methods 8015, 8020, and 8260. The three methods
listed use a flame ionization detector (FID), pho-
toionization detector (PID) and mass spectrometry
(MS) respectively. Because gasoline range organic
(GRO) samples can contain both petroleum and
oxygenate components, chromatographic resolution
is preferred regardless of the method used. One
example involves the compounds MTBE and
tert
-
butyl alcohol (TBA). Regulatory agencies recom-
mend adding TBA to the target list for contaminated
sites known to contain MTBE because it is both a
breakdown product of MTBE and a gasoline addi-
tive. Both MTBE and TBA respond on the PID
(Method 8020) and they share ions (MS by Method
8260), so MTBE and TBA must be resolved regard-
less of which detector is used.
The medium polarity Rtx
®
-VGC phase makes these
columns ideal for the analysis of both hydrocarbons
and oxygenates. The unique polarity of these
columns improves the separation of oxygenates,
which ensures more accurate detection when using
PID. Restek does not recommend using FID alone
for detecting these compounds.
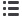
A 30m, 0.45mm ID, 2.55µm Rtx
®
-VGC column
helps determine low concentrations of oxygenates
in the presence of aliphatic compounds, resolving
MTBE from 2-methylpentane, 3-methylpentane, and
TBA (Figure 1). Furthermore, these optimized col-
umn dimensions allow the correct desorb flow
rates from the purge and trap, faster analyses times,
and better resolution of closely eluting peaks, com-
pared to tradional 0.53mm ID columns. The oxy-
genates can be identified by using MS detection
(Figure 2).
One commonly overlooked compound in the analy-
sis of GRO samples is chlorobenzene. Figure 1 does
not include chlorobenzene, however another analy-
sis under identical conditions shows the retention
time of chlorobenzene relative to ethylbenzene and
m/p
-xylene (Figure 3). Because the action limit for
chlorobenzene is many times lower than for ethyl-
benzene, these compounds must be resolved.
Environmental laboratories should keep in mind
that even if clients do not specifically request data
for chlorobenzene, these samples may require
reprocessing in the future to determine if
chlorobenzene is present. Without resolution of
these analytes, it may not be possible to use the PID
to provide such information.
The success of the GC/PID method is based on the
ability of the analytical column to resolve oxy-
genates from the early-eluting alkanes, alkenes,
and, to a lesser extent, alkynes. To minimize false
positive results for MTBE or other oxygenates, it is
important to separate 2-methylpentane and 3-
methylpentane. Non-polar phases (e.g., Rtx
®
-1 and
DB-MTBE columns) have been recommended for
separating these compounds. However, these phas-
es are incompatible with polar compounds, which
can result in broader peaks and lower capacity for
the alcohols. The Rtx
®
-VGC column will increase
your level of confidence in your analytical data and
prevent high bias. It is an ideal choice for analyzing
gasoline additives in GRO samples.
by Christopher English, Environmental Applications Chemist
✔
More accurate results through better resolution of target compounds.
✔
Determine low concentrations of oxygenates in the presence of aliphatic compounds.
✔
Resolve methyl-
tert
-butyl ether (MTBE) from target
tert
-butyl alcohol (TBA).
1 2
5
3
4
6
9
10
7
8
11
12
13 14
15, 16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
25
Column:
Rtx
®
-VGC 30m, 0.45mm, 2.55µm (cat.# 19408)
Inj.:
Each component 100ppb in 5mL of RO water, except
tert-
butyl alcohol 5000ppb; 2/1-methynaphthalene 150ppb;
ethyl methyl benzene 50ppb.
GC:
Finnigan 9001
Oven temp.:
40°C (hold 2 min.) to 130°C @ 6°C/min. (hold 0 min.) to 230°C @ 30°C/min. (hold 2 min.).
Carrier gas:
helium @ ~8mL/min.
Detector:
Finnigan PID, make up 7mL/min., purge 7mL/min., set @ 0.35mV, base temperature 200°C.
1. 2-methylpentane
2. 3-methylpentane
3. methyl-
tert
-buyl ether
4.
tert
-butyl alcohol
5. diisopropyl ether
6. ethyl
-
tert
-butyl ether
7. isooctane
8.
n
-heptane
9. benzene
10.
tert
-amyl-methyl ether
11.
α
,
α
,
α
-
trifluorotoluene
12. toluene
13. 1-chloro-3-fluorobenzene
14. ethylbenzene
15.
m
-xylene
16.
p
-xylene
17.
o
-xylene
18. isopropylbenzene
19. ethyl-methylbenzene
20. 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene
21. 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene
22. 4-bromochlorobenzene
23. naphthalene
24. 2-methylnaphthalene
25. 1-methylnaphthalene
GC_EV00465
19
min.
5
10
15
20
Figure 1
Use purge and trap concentration and an Rtx
®
-VGC column to resolve oxygenates
and other target gasoline compounds better than with other columns specifically
designed to resolve MTBE.
MTBE resolved from
2-methylpentane,
3-methylpentane,
and TBA