9
800-356-1688
•
VI.AnalysisofCollectedSamples
Once receivedby the lab,eachcanister is identified from the information in the
chain of custody report. The final pressure is checked to ensure no leaks
appearedduring transport. Itmight benecessary topressurize a canisterprior
to the analysis; do this by adding humidifiednitrogenor air to the canister to
a pressure greater than 5 psig or higher, depending on the sample volume
needed for analysisor for suitablydiluting the sample (e.g.,TableV).Theneed
to dilute is determined by the preconcentrator instrument. Some air precon-
centrators can be operated while the canister is under slight vacuum. Check
with your instrumentmanuals or with themanufacturer to determine if you
must dilute your samples prior to analysis. Dilution factors can be calculated
according toEquation3.
Toanalyze the sample,withdrawanaliquot of the sample from the canister.For low level ambient air analysis,withdraw250-500mL
of sample from the canister and concentrate the analytes by using amass flow controller and a cryogenically cooled trap (e.g., glass
beads and/or a solid sorbent).Desorb the concentrated analytes from the trap anddeliver them to a cryofocuser to focus the sample
bandwidth prior to introduction onto the GC column. A 60m x 0.32mm ID x 1.0 µmRtx®-1 column typically is used for EPA
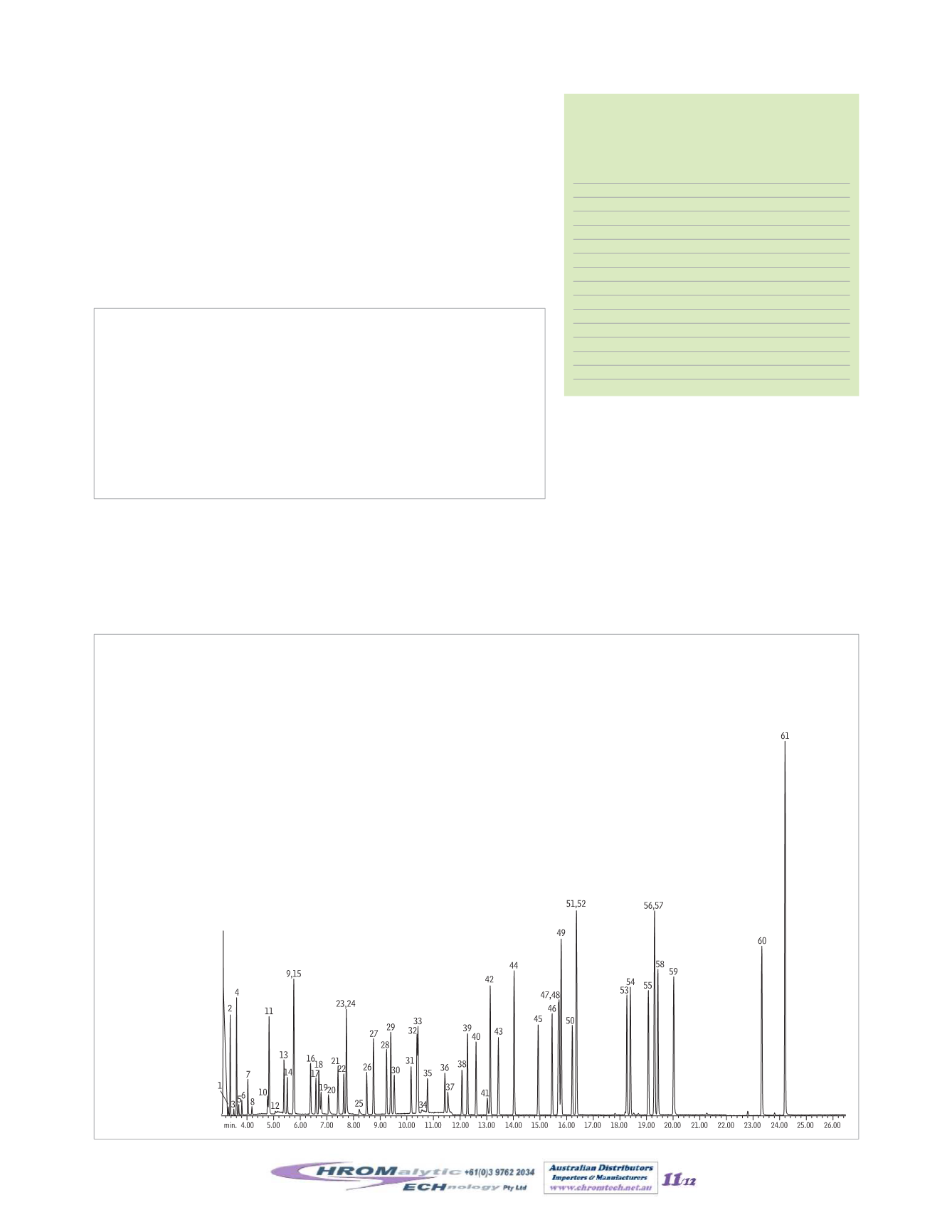
MethodTO-14AorMethodTO-15 ambient air analysis; anMSD is a commondetector. Figure 9 shows a typical TIC spectrum for
aTO-15 ambient air analysis.
TableV
Dilution factors toadjust final
samplingpressure to
14.7psig
fora
6-liter canister.
Final Vacuum Sample Volume
Dilution
("Hg)
(liters)
Factor
29
0
63.77
27
0.58
20.37
25
0.99
12.12
23
1.39
8.63
20
1.99
6.02
17
2.59
4.63
15
2.99
4.01
12
3.59
3.34
10
3.99
3.00
7
4.60
2.61
5
5.0
2.40
3
5.40
2.22
0
6
2.00
Equation3:
dilution factor= (P
after dilution
+P
lab atmosphere
) / (P
lab atmosphere
- P
before dilution
)
The dilution factor is calculated from the post-sampling pressure (before dilu-
tion), the final pressure (afterdilution), and theatmosphericpressure in the lab-
oratory.The factor for converting "Hg to psi= 0.491.
Example: At the end of a sampling period the gauge pressure in a canisterwas
-7 "Hg.The canisterwas pressurizedwith nitrogen to 14.7 psig (1Atm.).
The dilution factor is (14.7+ 14.7) / (14.7 - (7 x 0.491))= 2.61
Figure9
USEPATO-15ambient air analysis.
Column:
Rtx
®
-1, 60m, 0.32mm ID, 1.0µm (cat.# 10157)
Sample:
TO-15 standard (cat.# 34436) humidified to 33%RH in a 6L SilcoCan
®
canister (cat.# 24182)
Concentrator:
Nutech 3550A Preconcentrator; 300mL sample concentrated at
-160°C, thermally desorbed at 150°C, cryofocused at -185°C,
thermally desorbed to column at 150°C
Carrier gas:
helium, constant flow
Flow rate:
1.2mL/min.
Oven temp.:
30°C (hold 4min.) to 175°C@ 8°C/min., to 220°C@
20°C/min. (hold 2min.)
Det.:
MS
Transfer line
temp.:
150°C
Scan range:
35–280amu
Ionization:
EI
Mode:
scan
1. propylene
2. Freon
®
-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane)
3. chloromethane
4. Freon
®
-114 (dichlorotetrafluoroethane)
5. vinyl chloride
6. 1,3-butadiene
7. bromomethane
8. chloroethane
9. carbon disulfide
10. acetone
11. Freon
®
-11 (trichlorofluoromethane)
12. isopropyl alcohol
13. 1,1-dichloroethene
14. methylene chloride
15. Freon
®
-113
(1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane)
16.
trans
-1,2-dichloroethene
17. 1,1-dichloroethane
18. methyl
tert
-butyl ether
19. vinyl acetate
20. methyl ethyl ketone
21.
cis
-1,2-dichloroethene
22. hexane
23. chloroform
24. ethyl acetate
25. tetrahydrofuran
26. 1,2-dichloroethane
27. 1,1,1-trichloroethane
28. benzene
29. carbon tetrachloride
30. cyclohexane
31. 1,2-dichloropropane
32. trichloroethylene
33. bromodichloromethane
34. 1,4-dioxane
35. heptane
36.
cis
-1,3-dichloropropene
37. methyl isobutyl ketone
38.
trans
-1,3-dichloropropene
39. 1,1,2-trichloroethane
40. toluene
41. methyl butyl ketone
42. dibromochloromethane
43. 1,2-dibromoethane
44. tetrachloroethylene
45. chlorobenzene
46. ethylbenzene
47.
p
-xylene
48.
m
-xylene
49. bromoform
50. styrene
51.
o
-xylene
52. 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane
53. 4-ethyltoluene
54. 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene
55. 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene
56. 1,3-dichlorobenzene
57. benzyl chloride
58. 1,4-dichlorobenzene
59. 1,2-dichlorobenzene
60. 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene
61. hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
GC_AR00748
Website :
E-mail :
TelNo : 03 9762 2034 . . . inAUSTRALIA


