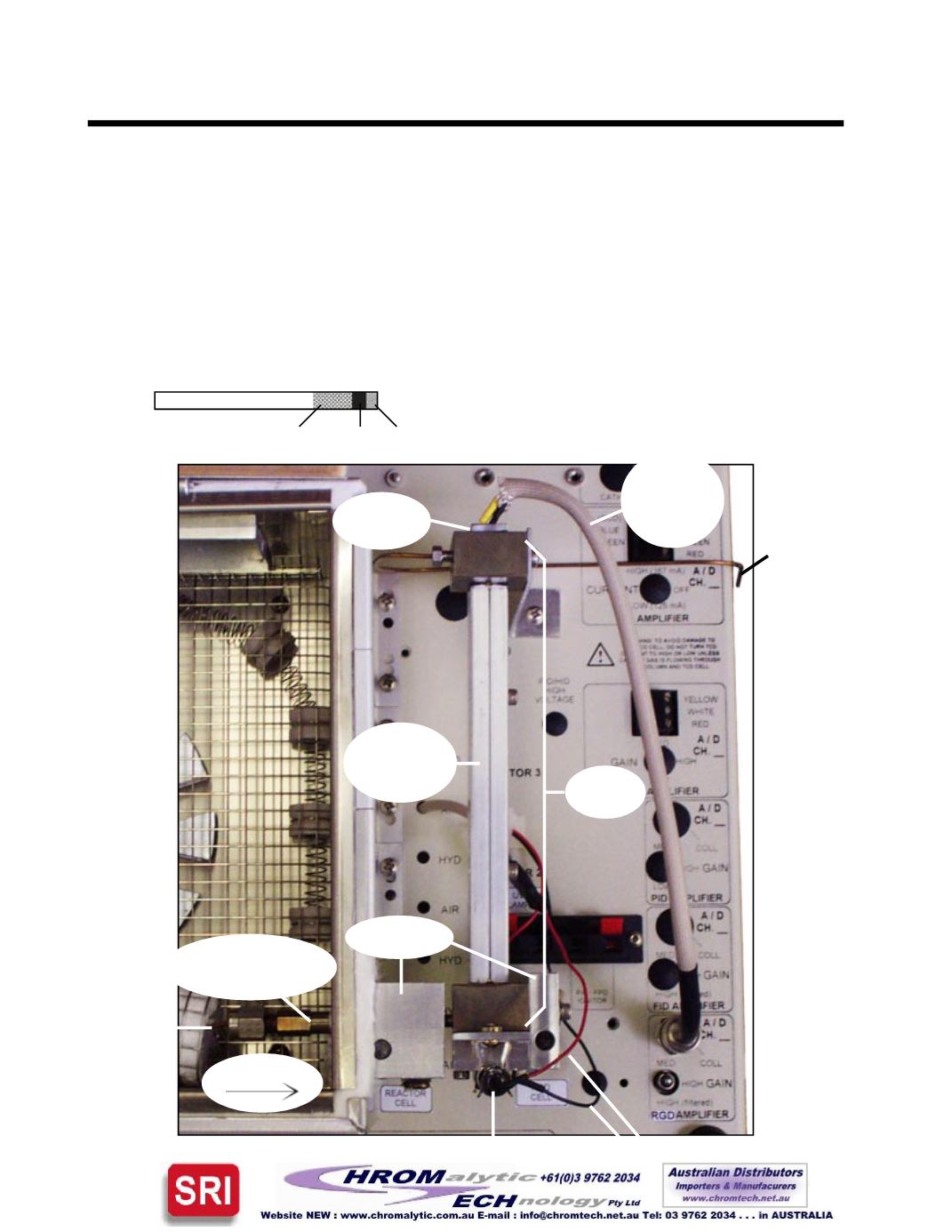
GC DETECTORS
Reduction Gas Detector - RGD
Theory of Operation
TheSRIRGDdetector uses amercuricoxide (HgO) reaction tube and amercury lamp in aheatedUV
detectorcell. The reaction tube isheated to260-300
o
C. Located immediatelydownstreamof the reaction
tube, theUVdetectorcell isheated to170
o
C. TheUVdetectorcell isequippedwithamercury lampanda
UVphotodiode.Whenareducinggassuchascarbonmonoxideelutesfrom theGCcolumn, itreactswith the
HgO toformgaseousmercuryvapor,which is thenswept into theUVcell.Thegaseousmercuryabsorbs the
UV light from themercury lampas it flows through thecell.Thechange in transmittance isconvertedby the
datasystem intoanabsorbanceoutput (1.00voltperabsorbanceunit),which is linearlyproportional to the
amountofreducinggas.
Detector cell
exit tube
Photodiode
lead
toamplifier
Heaterblocks
RGD jetwithHgO
reactor tube inside
Sample flow
Detector
cell
Photodiode
detector
Leads to lamppower terminal
Mercury lamp
Column
Optical path
withheater
clam shell
RGD reactor tube
Quartzwool
HgO Frit
CO+HgO=CO
2
+Hg (vapor)
H
2
+HgO=H
2
O+Hg (vapor)


