When performing GC/MS analysis of drugs, many chemists choose to derivatize samples prior to analysis. Derivatization not only increases the volatil-
ity of some drug compounds, but it also reduces activity, resulting in improved peak shape andmore accurate quantification. An additional advantage
is that derivatized compounds have a higher molecular weight, thus producing more reliable mass spectra than underivatized compounds. Despite
these benefits, derivatization reagents are often
harsh and can damage analytical columns, lead-
ing to high bleed, significant reduction in reten-
tion times, and increased tailing for active com-
pounds. Often, this damage is concentrated
near the head of the column, so trimming a
short length can improve results. However, trim-
ming is a finite solutionas repeated clippingulti-
mately results in decreased efficiency and short-
er column lifetimes. Choosing a more rugged
column, such as the Rxi®-5Sil MS column, is a
better alternative. The Rxi®-5Sil MS column is
extremely stable and holds up to harsh treat-
ment, including repeated exposure to derivati-
zation reagents.
The analysis of amphetamine illustrates the
ruggedness of the arylene-based Rxi®-5Sil MS
polymer. Amphetamine is typically derivatized,
because the underivatized form is an active
basic compound that produces only a few low
molecular weight ions for monitoring. In con-
trast, upon derivatization, activity decreases,
resulting in dramatically improved peak shape
and more accurate quantitation. Additionally,
several higher molecular weight ions are pro-
duced, which can be monitored for definitive
identification.
By Amanda Rigdon, Clinical/Forensic Innovations Chemist and Gary Stidsen, GC Columns Product Marketing Manager
• Save costs with long column lifetime.
• Reduce downtime from column trimming and replacement.
• Improve peak shape for active compounds.
Clinical Forensic
Column:
Rxi
®
-5Sil MS, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm (cat.# 13623)
Sample:
Column Test Mix (cat.# 35226)
Inj.:
1.0 µL split (split ratio 1:60), 4 mm recessed
gooseneck liner (cat.# 20983)
Inj. temp.:
250 °C
Carrier gas:
helium, constant pressure
Linear velocity: 36 cm/sec @ 125 °C
Oven temp.:
125 °C
Det:
FID @ 320 °C
Instrument:
Agilent 6890
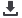
1. 2-ethylhexanoic acid
2. 1,6-hexanediol
3. 4-chlorophenol
4. tridecane
5. 1-methylnaphthalene
6. 1-undecanol
7. tetradecane
8. dicyclohexylamine
Figure 1
Rugged Rxi®-5Sil MS columns produce consistent retention times, even after
400 injections of derivatization reagent.
GC_CF01131
Rugged Rxi®-5Sil MS Columns Stand up to Derivatization
Reagents, Reducing Downtime and Replacement Costs
16
www.restek.comWebsite :
www.chromtech.net.auE-mail :
info@chromtech.net.auTelNo : 03 9762 2034 . . . in AUSTRALIA