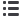
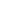
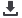
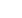
Figure 1
Separate difficult PAHs easily using a 30m x 0.25mm ID x 0.25μm Rxi®-5Sil MS column.
•
4
•
2007 vol. 4
Environmental
Rxi®-5Sil MS columns are ideal for the analysis of semivolatile analytes such as those found in EPA Method 8270. Low bleed profiles
assure accurate quantification of late eluting compounds, such as polycyclic (polynuclear) aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), includ-
ing the challenging separation of benzo(b)fluoranthene and benzo(k)fluoranthene (Figures 1 and 2). The inertness of the Rxi®-5Sil
MS column is demonstrated through the peak shapes and responses of active analytes, such as pyridine (basic) and 2,4-dinitrophe-
nol (acidic), at low levels. Peak symmetry is good and analyte responses exceed method requirements even at single ng on-column
levels (Figure 3). Chromatography, and thus quantification, of many active semivolatile compounds is improved by the inertness of
Rxi®-5Sil MS columns.
The Rxi®-5Sil MS columns most commonly used for semivolatiles analysis are the 30m x 0.25mm ID columns with either 0.25µm
or 0.5µm film thicknesses. These dimensions generally offer the best balance of sample capacity, analysis time, and column lifetime.
However, if sample throughput is paramount, shorter narrow bore columns, such as the 20m x 0.18mm ID with either 0.18µm or
0.36µm film thicknesses, are preferred. Due to increased peak efficiencies, temperature programs can be accelerated without com-
promising key separations. Regardless of which dimension you choose, the new Rxi®-5Sil MS columns are ideal for analyzing semi-
volatile compounds.
Fast, Accurate Semivolatiles Analysis
Continued from page 3.
GC_EV00943
EIC
Excellent
resolution
of PAHs
Excellent
peak shape
of pyridine
Excellent
response for
2,4-dinitrophenol
RF=0.245
Extracted ion
@184m/z
1. 1,4-dioxane
2.
n
-nitrosodimethylamine
3. pyridine
c. toluene
4. 2-fluorophenol (SS)
5. phenol-d6 (SS)
6. phenol
7. aniline
8. bis(2-chloroethyl) ether
9. 2-chlorophenol
10. 1,3-dichlorobenzene
11. 1,4-dichlorobenzene-d4 (IS)
12. 1,4-dichlorobenzene
13. benzyl alcohol
14. 1,2-dichlorobenzene
15. 2-methylphenol
16. bis(2-chloroisopropyl) ether
17. 4-methylphenol/3-methylphenol
18.
n
-nitroso-di-
n
-propylamine
19. hexachloroethane
20. nitrobenzene-d5 (SS)
21. nitrobenzene
22. isophorone
23. 2-nitrophenol
24. 2,4-dimethylphenol
25. benzoic acid
26. bis(2-chloroethoxy)methane
27. 2,4-dichlorophenol
28. 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene
29. naphthalene-d8 (IS)
30. naphthalene
31. 4-chloroaniline
32. hexachlorobutadiene
33. 4-chloro-3-methylphenol
34. 2-methylnaphthalene
35. 1-methylnaphthalene
36. hexachlorocyclopentadiene
37. 2,4,6-trichlorophenol
38. 2,4,5-trichlorophenol
39. 2-fluorobiphenyl (SS)
40. 2-chloronaphthalene
41. 2-nitroaniline
42. 1,4-dinitrobenzene
43. dimethyl phthalate
44. 1,3-dinitrobenzene
45. 2,6-dinitrotoluene
46. 1,2-dinitrobenzene
47. acenaphthylene
48. 3-nitroaniline
49. acenaphthene-d10 (IS)
50. acenaphthene
51. 2,4-dinitrophenol
52. 4-nitrophenol
53. 2,4-dinitrotoluene
54. dibenzofuran
55. 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorophenol
56. 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol
57. diethyl phthalate
58. 4-chlorophenyl phenyl ether
59. fluorene
60. 4-nitroanaline
61. 4,6-dinitro-2-methylphenol
62.
n
-nitrosodiphenylamine
(diphenylamine)
Column: Rxi
®
-5Sil MS, 30m, 0.25mm ID, 0.25µm (cat.# 13623)
Sample: US EPA Method 8270D Mix, 1µL of 10µg/mL (IS 40µg/mL), 8270 MegaMix
®
(cat.# 31850), Benzoic Acid (cat.# 31879), 8270 Benzidines Mix
(cat.# 31852), Acid Surrogate Mix (4/89 SOW) (cat.# 31025), Revised B/N Surrogate Mix (cat.# 31887), 1,4-Dioxane (cat.# 31853), SV Internal Standard
Mix (cat.# 31206); Inj.: 1.0µL (10ng on-column concentration), 4mm Drilled Uniliner
®
(hole near bottom) inlet liner (cat.# 20756), pulsed splitless: pulse
25psi @ 0.2 min., 60mL/min. @ 0.15 min.; Inj. temp.: 250°C; Carrier gas: helium, constant flow; Flow rate: 1.2mL/min.; Oven temp.: 40°C (hold 1.0 min.)
to 280°C @ 25°C/min. to 320°C @ 5°C/min. (hold 1 min.); Det.: MS; Transfer line temp: 280°C; Scan range: 35-550amu; Ionization: EI; Mode: scan
63. 1,2-diphenylhydrazine (as
azobenzene)
64. 2,4,6-tribromophenol (SS)
65. 4-bromophenyl phenyl ether
66. hexachlorobenzene
67. pentachlorophenol
68. phenanthrene-d10 (IS)
69. phenanthrene
70. anthracene
71. carbazole
72. di-
n
-butyl phthalate
73. fluoranthene
74. benzidine
75. pyrene-d10 (SS)
76. pyrene
77.
p
-terphenyl-d14 (SS)
78. 3,3'-dimethylbenzidine
79. butyl benzyl phthalate
80. bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate
81. 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine
82. benzo(a)anthracene
83. bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
84. chrysene-d12 (IS)
85. chrysene
86. di-
n
-octyl phthalate
87. benzo(b)fluoranthene
88. benzo(k)fluoranthene
89. benzo(a)pyrene
90. perylene-d12 (IS)
91. dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
92. indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene
93. benzo(ghi)perylene
c = contaminant
EIC