AdvancedGasChromatography–Progress inAgricultural, Biomedical and Industrial Applications
34
There are also supports of other types, but these are much less used. Such supports are
basedon syntheticpolymers (i.e. Teflon), glass andothers.
Next will be presented several examples of a few illustrative applications of some
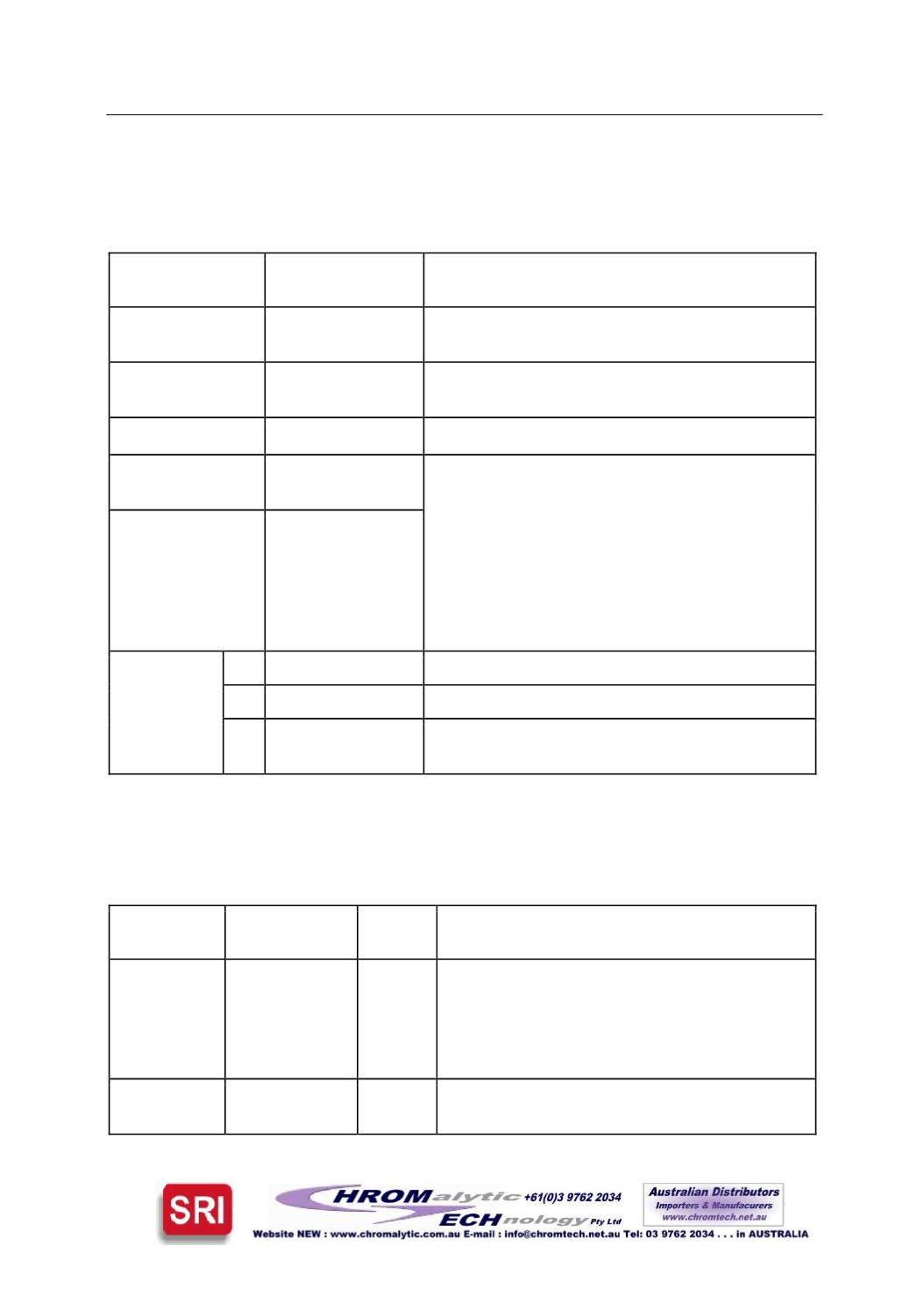
adsorbents (Poole, 2003) Table 2:
StationaryPhase
Maximum
Temperature (°C)
UsualApplications
Alumina
200
Alkanes, alkenes, alkines, aromatichydrocarbons -
fromC
1
toC
10
Silicagel
250
Hydrocarbons (C
1
–C
4
), inorganic gases, volatile
ethers, esther andketone
Carbon
350
Inorganic gases, hydrocarbons (C
1
-C
5
)
Carbonmolecular
sieves
150
Oxygenated compounds (C
1
-C
6
)
Molecular sieves
(5X and 13X)
350
Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen,methane,
noblegases. SeparationHe/Ar andAr/O
2
.
HydrocarbonsC
1
–C
3
on 3X, on 13X till C
12
but no isomers. Cyclodextrine, halocarbons,
permanent gases, hydrofluorocarbons,
hydrocarbonsC
1
-C
10.
Q
310
HydrocarbonsC
1
-C
10
, halocarbonsC
1
-C
2
.
S
250
Volatileorganic solventsC
1
–C
6
U
190
Nitrocompounds, nitrils,water,
inorganic gases.
Table 2. Illustrative examples of some adsorbents and temperaturevalues atwhich theyare
active
Table 3 brieflypresents some gas chromatographymain adsorbents’ characteristics (Grob&
Barry, 2004).
Adsorbent
Polymeric
material
Tmax, °C
Applications
HayeSepA
DVB-EGDMA
165
Permanent
g
ases, includin
g
: h
y
dro
g
en, nitro
g
en,
oxygen, argon, CO, andNO at ambient
temperature; can separateC2hydrocarbons,
hydrogen sulphide andwater at elevated
temperatures
HayeSepB
DVB-PEI
190
C1 andC2 amines; trace amounts of ammonia
andwater


