556
GC CHROMATOGRAMS |
ENVIRONMENTAL
Semivolat i les
Peak List
Retention Time
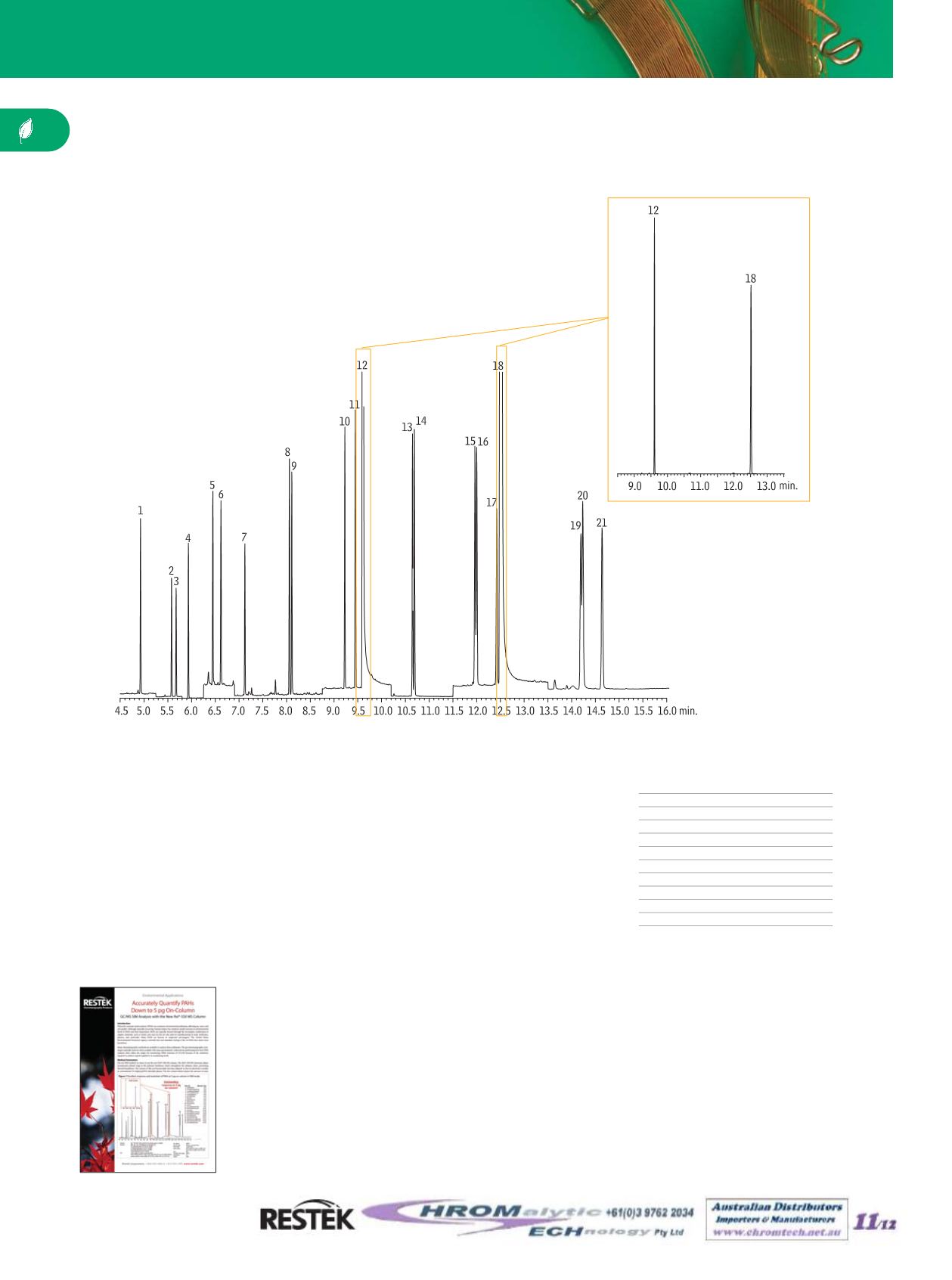
1. naphthalene
4.93
2. 2-methylnaphthalene
5.58
3. 1-methylnaphthalene
5.68
4. 2-fluorobiphenyl (SS)
5.93
5. acenaphthylene
6.45
6. acenaphthene
6.62
7. fluorene
7.12
8. phenanthrene
8.06
9. anthracene
8.11
10. fluoranthene
9.23
11. pyrene
9.45
12.
p
-terphenyl-d14 (IS)
9.61
13. benzo(a)anthracene
10.65
14. chrysene
10.69
15. benzo(b)fluoranthene
11.96
16. benzo(k)fluoranthene
12.00
17. benzo(a)pyrene
12.42
18. perylene-d12 (IS)
12.51
19. indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene
14.19
20. dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
14.23
21. benzo(ghi)perylene
14.65
Column:
Rxi
®
-5Sil MS, 30m, 0.25mm ID, 0.25µm (cat.# 13623)
Sample:
PAH mix, 1µL of 0.005µg/mL (IS 2µg/mL)
SV Calibration Mix #5 (cat.# 31011)
1-methylnaphthalene (cat.# 31283)
2-methylnaphthalene (cat.# 31285)
2-fluorobiphenyl (cat.# 31091)
Inj.:
1.0µL (5pg on-column concentration),
4mm Drilled Uniliner
®
(hole near top) inlet liner w/wool (cat.# 21055-200.5),
pulsed splitless: pulse 20psi @ 0.2 min., 60mL/min. @ 0.15 min.
Inj. temp.:
300°C
Carrier gas:
helium, constant flow
Flow rate:
1.4mL/min.
Oven temp.:
50°C (hold 0.5 min.) to 290°C @ 25°C/min. to 320°C @ 5°C/min.
Det.:
MS
Transfer line
temp:
290°C
Ionization:
EI
Mode:
SIM
Single Ion Monitoring Program
Group Time Ion(s)
Dwell (ms)
1
4.00
128
100
2
5.25
142
100
3
5.80
172
100
4
6.25
152
100
5
6.90
166
100
6
7.60
178
100
7
8.75 202, 244
100
8
10.2
228
100
9
11.5 252, 264
100
10
13.5 276, 278
100
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Rxi®-5Sil MS
GC_EV00970
Full Scale
Outstanding response at
5pg on-column!
Rxi® Technology!
Exceptionally inert,
ultra low- bleed
capillary columns.
free
literature
Accurately Quantify PAHs Down to 5 pg On-Column: GC/MS Sim Analysis with the New Rxi®-5Sil MS Column
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are common environmental pollutants, affecting air, water, and soil quality.
Although naturally occurring, human impact has created a steady increase in environmental levels of PAHs and their
byproducts. PAHs are typically formed through the incomplete combustion of organic materials, such as wood, coal,
and oil, but are also used in manufacturing of some medicines, plastics, and pesticides. Many PAHs are known or
suspected carcinogens. The United States Environmental Protection Agency currently lists and mandates testing of
the 16 PAHs they deem most hazardous.
Download your free copy from
Applications Note
lit. cat.# EVAN1284
Website :
E-mail :
TelNo : 03 9762 2034 . . . in AUSTRALIA
Mar 2011


