• 6 •
800-356-1688
Variousmethods have provided guidelines for
GC/electron capture detection (GC/ECD) analysis of
organochlorine pesticides and PCBs in aqueous and
soil matrices. Pesticides and PCB congeners now are
analyzed by separatemethods, to ensuremore accu-
rate PCB data and eliminate complications that arise
in combined analysis. Analyses of individual PCB
congeners greatly simplify quantitative studies, and
improve data, relative to the difficult quantitative
studies of PCBs asmixtures (e.g., Aroclor
®
mix-
tures)—especially withmixtures weathered by long
exposure in the environment.
GC analysis of organochlorine pesticides and PCBs
can be very challenging because of lengthy calibra-
tions, linearity problems, and potential breakdown
of some of the pesticides. In addition to adequate
resolution of the target analytes, the column for this
analysismust exhibit low bleed. Awide-bore
(0.53mm ID) column is listed in US EPAMethods
8081A and 8082A for organochlorine pesticides,
but a narrow-bore columnmay be used in single-
column analyses. Our new 0.32mm ID, 0.5µm
phase Rtx
®
-XLB column is ideal for analyses of
active compounds, due to improvements in polymer
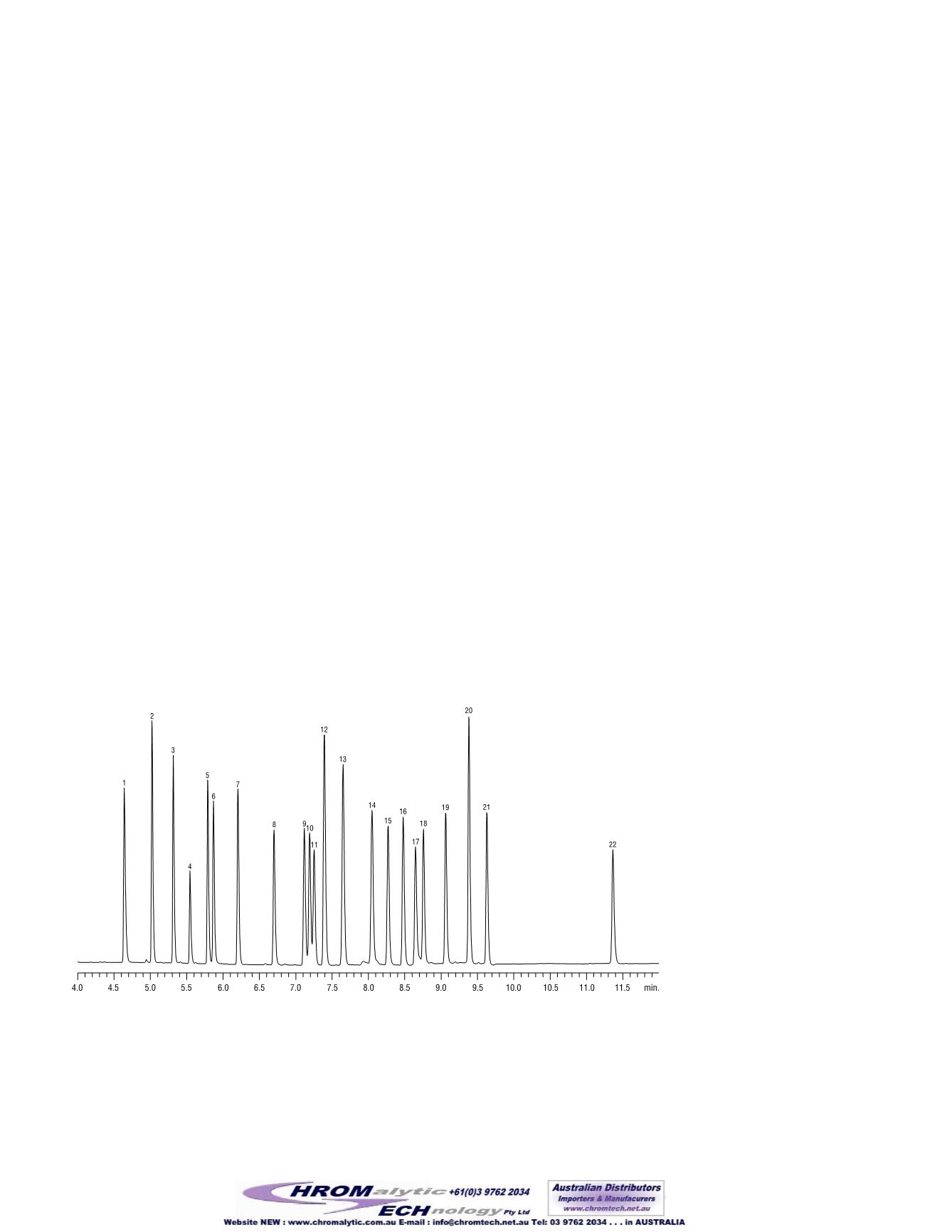
synthesis and tubing deactivation. Figure 1, an
analyses of 20 organochlorine pesticides
(Organochlorine PesticideMix AB #2, cat.#
32292), demonstrates the superior efficiency and
low bleed characteristic of the new column, even at
330ºC. The column, in combinationwith a high ini-
tial temperature, 120ºC, reduced analysis time to
11.5minutes, with excellent separation. Very low
bleed and high thermal stability ensure reliable
detection at the 80/160/800 ppb level. The very low
bleed alsominimizes detector contamination, pro-
longing intervals between cleanings and thus
increasing throughput over time. Note that tomini-
mize breakdown of labile pesticides weminimized
sample contact withmetal surfaces by using a
Drilled Uniliner
®
inlet liner to convey the sample
directly onto the column.
Restek chemists carefully reviewed EPAMethods
8080 and 8081A, then developed three calibration
mixes that include 20most oftenmonitored
organochlorine pesticides. Themix used to obtain
Figure 1 has varied concentrations of the target ana-
lytes, from 8 to 80µg/mL, because these pesticides
exhibit significantly differing responses.* The other
twomixes include the 20 analytes at a single concen-
tration, 200µg/mL or 2000µg/mL. The 2000µg/mL
concentration often ismore practical than lower
concentrations, especially if several mixesmust be
combined. We also offer all surrogates and internal
standards currently required for these analyses.
PCBs are persistent in the environment, and accu-
rately determining their presence and concentrations
is very important. A common question is whether
such analyses should be focused onmixtures of
PCBs (e.g., Aroclor
®
mixes) or on individual con-
geners. Congener-specific analyses have important
advantages over analyses of mixtures: generally, con-
gener analyses offer lower detection limits and
greater information content. In addition, composi-
tions of weathered, degraded, andmetabolized PCB
mixtures can bemeasured and interpretedmore
easily. Also, it is easier to detect interferences caused
by other chemicals, and quantification of individual
congeners ismore accurate. However, coelution of
analytes is a problem in a PCB congener analysis, so
a strong quality assurance program and reliable ref-
erencematerials are needed by the analyst. To facili-
tate congener-specific analyses, we nowmake a ref-
erencemix of 19 PCB congeners at 100µg/mL each
in isooctane, suitable for EPAMethod 8082A.
Depending on regulatory and project requirements,
GC/ECDAnalysis of Organochlorine Pesticides or
Polychlorinated Biphenyls
Using a Low-Bleed Rtx
®
-XLBColumn and Restek ReferenceMaterials
by Greg France, Innovations Chemist, Gary Stidsen, Innovations TeamManager,
and KatiaMay, Ph.D., Senior R&DChemist
✔
Rtx
®
-XLB column shows extremely low bleed and excellent inertness, improving sensitivity
for active compounds.
✔
20 common organochlorine pesticides in 3 convenient reference concentrations.
✔
19USEPAMethod 8082APCB congeners in one solution.
Figure1
Organochlorinepesticides separated in less than12minutes, usinganRtx®-XLB column.
1. 2,4,5,6-tetrachloro-
m
-xylene (ss)
2.
α
-BHC
3.
γ
-BHC
4.
β
-BHC
5.
δ
-BHC
6. heptachlor
7. aldrin
8. heptachlor epoxide
9.
γ
-chlordane
10.
α
-chlordane
11. endosulfan I
12. 4,4'-DDE
13. dieldrin
14. endrin
15. 4,4'-DDD
16. endosulfan II
17. endrin aldehyde
18. 4,4'-DDT
19. endosulfan sulfate
20. methoxychlor
21. endrin ketone
22. decachlorobiphenyl (ss)
Rtx
®
-XLB 30m, 0.32 ID, 0.5µm (cat.# 12839)
Sample:
OrganochlorinePesticideMixAB (cat.#32292) 80/160/800ppb inhexane
2,4,5,6-tetrachloro-
m
-xylene (cat.# 32027) surrogate, 80ppb
decachlorobiphenyl (cat.# 32029) surrogate, 160ppb
Inj.:
1.0µL splitless (0.75min. hold), 4mmDrilledUniliner
®
inlet liner (cat.# 21055)
Inj. temp.:
220°C
Carrier gas:
hydrogen, constant pressure
Linear velocity: 60cm/sec. @ 120°C
Oven temp.:
120°C (hold 0.5min.) to 260°C@ 29°C/min. (hold 2.5min.), to 330°C@ 28°C/min. (hold 3min.)
Det.:
ECD@ 320°C
GC_EV00720
*Formix composition, see page 8 of this
Advantage.


