10
Figure3.
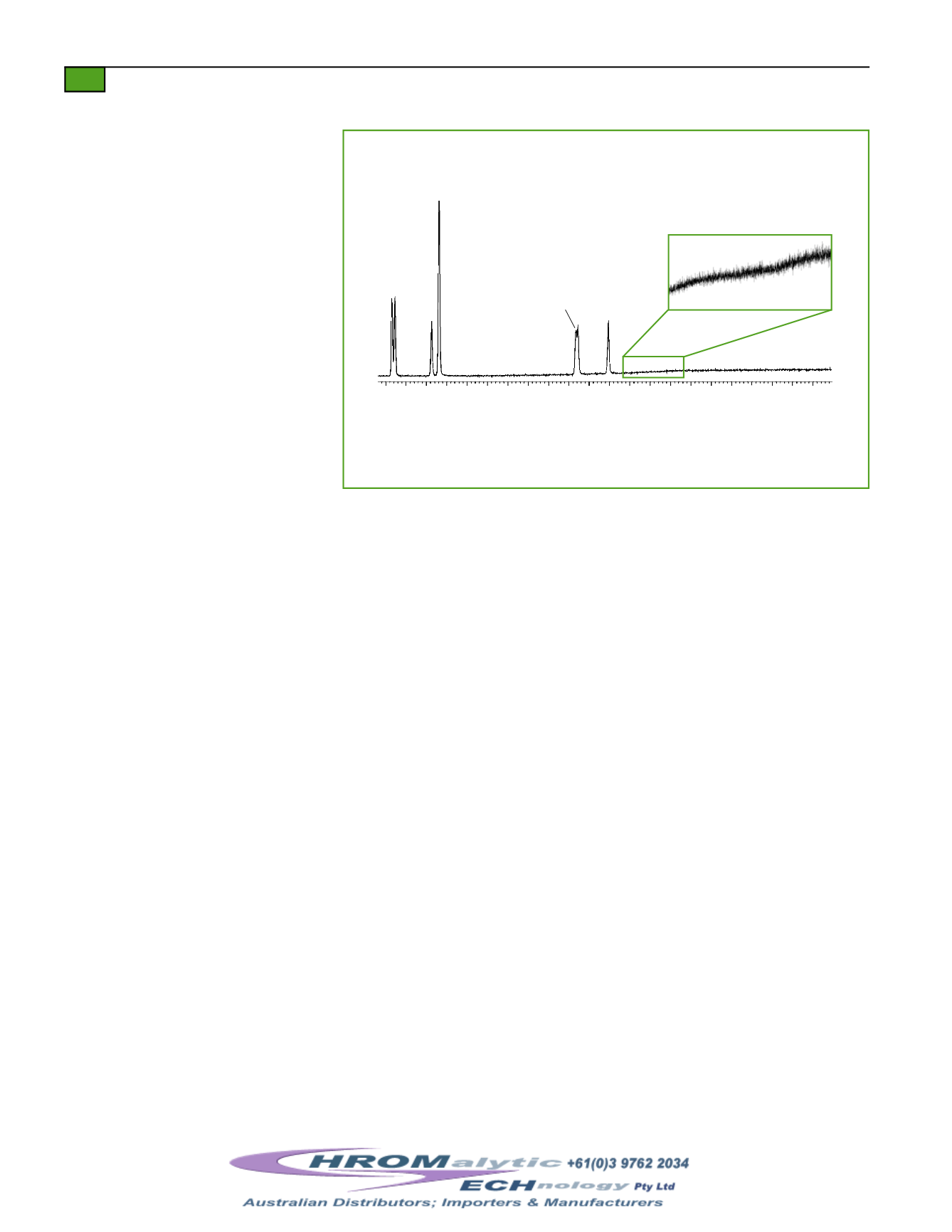
TheRtx
®
-5SilMS column exhibits lowbleed at 20ng concentration level.
Detector saturationalsocanbecausedby theconcentrationof theanalytes. Itwas common
practiceonolder, less sensitiveGC/MS systems to increase themultiplier voltageabove the tune
value to improve sensitivityof low-concentration standards.This techniquecan lead toproblems
with thenewer,more sensitive instruments. It ismuchmore likely thehigher concentration
calibration standardswill saturate thenewGC/MS systems. Itmaybenecessary to reduce the
multiplier voltagebelow the tunevalue if high-end roll-off isobserved.High-end roll-off also
maybeobservedwhenusingpressure-pulsing injection techniques tominimizehighmolecular
weight discrimination. If this isobserved, youmayeither increase the stationaryphase film
thickness, or increase thecolumndiameter.Alternatively, youmaymodify the injection
conditions toeliminate the sourceof theoverload.
Columncapacity
alsomust beaddressedwhenoptimizing theanalysis.The typical calibration
range formanyof thesemethods is20 to160ngper compound.This requires acolumn stationary
phaseanddiameter thatwill not overloadwitha160ngor larger injection.Because there is a loss
of analyte inany splitless injection, calculationof thenecessarycolumncapacity isnot simple. If
the injectionhasbeenoptimized for splitlesshold-timeand fused silicawool isbeingused in the
liner tominimizehighmolecularweight discrimination, then it is easier tooverload theanalytical
column. Possibly thebiggest causeof overload is frompressure-pulsing the injectionport, as this
improves the transfer of all compounds to thecolumn.The requiredcapacity for your systemwill
bea functionof the specificcalibration standards and,more importantly, the injectionport.
From a capacity consideration, a 0.25mm ID columnwith0.25µm film thickness does not
have sufficient capacity for a 160ngper component standard. Figure4a shows the poor peak
shapeobservedwhen a column is overloaded. Increased capacity canbe achievedby
increasing columndiameter or film thickness.
When increasingcolumndiameter, the flow rateof thecolumncanbeaconcernwithbench-top
GC/MS systems.Manybench-topGC/MS systemsdonot have thepumpingcapacity for the
carrier gas flow that isneededwitha0.32mm IDcolumn.A0.28mm IDcolumncan increase
samplecapacitywithout exceeding thepumpingcapacityofmost bench-topGC/MS systems,
making it ideal for calibrating semivolatilecompounds from20 to160ngwithout overload.
Alternatively, a0.25mm IDcolumnwitha0.5µm film thickness alsohas sufficient capacity to
handleacalibration from20 to160ngwithout exhibitingoverload. Figure4b shows excellent
peak shape for a160ng-per-component standardona30m, 0.25mm ID, 0.5µmRtx
®
-5SilMS
column.
The total
analysis time
shouldbe as short as possiblewithout sacrificing separationor
resolutionbetween compoundswith similarmass spectra. Payparticular attention to the
separationbetweenbenzo-b- andbenzo-k-fluoranthrene—they tend tobe themost difficult-
1 2
3
4
5
6 7
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 min.
1. benzo(b)fluoranthene
2. benzo(k)fluoranthene
3. benzo(a)pyrene
4. perylene-d12
5. indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene
6. dibenz(a,h)anthracene
7. benzo(g,h,i)perylene
30m, 0.25mm ID, 0.5µmRtx
®
-5SilMS (cat#12738)
20ng splitless injectionof CLP standard;
GC:
HP/Agilent 6890w/ 5973mass selective detector, scan range 35-550
AMU;
Ovenprogram:
40°C (hold2min.) to290°C@20°C/min. (hold0 min.) to303°C@2°C/min. (hold0min.) to
330°C@6°C/min. (hold1min.);
Carrier gas:
He@1.0mL/min. constant flow;
Inj. temp.:
300°C;
Det. temp.:
280°C
Website :
E-mail :
TelNo : 03 9762 2034 . . . inAUSTRALIA


