○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
3
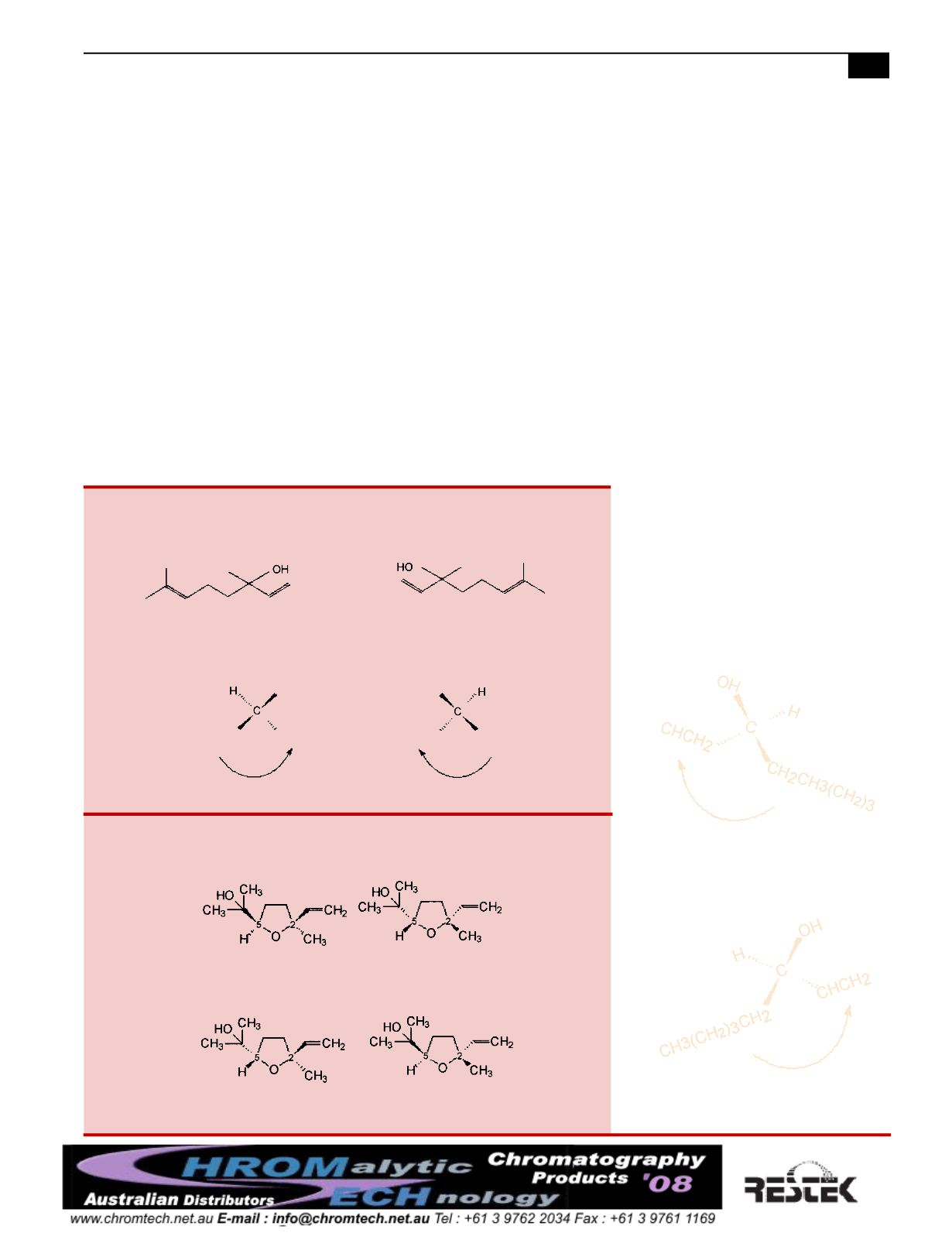
Linalool is a chiral compound because it contains an assymmetric carbon
center. Themirror images are not superimposable and so they are enanti-
omers.
S configuration
Enantiomers can be distinguished by configuration. Following groups from
high to low priority in the clockwise direction is denotedR, and S for the
counterclockwise direction.
R configuration
Figure 1A
Linalool oxides have two chiral centers at carbon numbers 2 and 5 and
exist as four enantiomers.
Figure 1B
2S, 5R
(+)-cis-linalool oxide
2R, 5S
(-)-cis-linalool oxide
2S, 5S
(-)-trans-linalool oxide
2R, 5R
(+)-trans-linalool oxide
WHATARECHIRAL
COMPOUNDS?
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Any carbon atom that is bonded to
four different functional groups is
termedachiral or anassymetriccar-
bon. Molecules containing one or
moreof thesecarboncentersarecon-
sidered chiral molecules. Chiral cen-
ters can exist in two forms called
enantiomers. These two forms are
non-superimposablemirror imagesof
each other, but both have similar
properties. For example, both enan-
tiomers will have the same boiling
point,densities,andreactionratesas
achiralmolecules. They do, however,
generallypossessdifferentaromaand
flavor characteristics; more impor-
tantly, they possess differences in
toxicity and biological activity.
Enantiomers are also known as opti-
cal isomersbecause they rotateplane
polarized light indifferent directions.
Optical isomers that rotate plane po-
larized light to the right, orclockwise,
are termed dextrorotary {denoted as
(d) or (+)}, Optical isomers that rotate
in the leftdirectionare termed levoro-
tary {denoted (l) or (-)}.
Enantiomers can be denoted by the
specific configuration around the
chiral center. Groups on the carbon
centerareassigneda “priority”based
onatomicnumber of the first bonded
atom (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules). The
group with the highest atomic num-
ber is rated first. If priority cannot be
establishedwith the first atom, work
outwarduntil prioritydifferencescan
be determined. Once priorities have
been established for all four groups,
specific configuration can be deter-
mined. An R configuration is desig-
nated when the priority around the
assymmetric carbon is ina clockwise
direction,whereasacounterclockwise
direction isdenotedasS. (
Figure1A
)
1
A chiral compound canpossessmul-
tiple chiral centers andmany combi-
nations of configurations. Linalool
oxidespossess two chiral centers, re-
sulting in four enantiomers. (
Figure
1B
)Note that configuration (RorS) is
independent fromopticalactivity (+or
-) or interactionwith plane-polarized
light.
CH
3
(CH
2
)
3
CH
2
CH
2
(CH
2
)
3
CH
3
CHCH
2
CH
2
CH
OH
HO
WHATARECHIRAL
COMPOUNDS?
Any carbon atom that is
bonded to four different groups
is termed a chiral or an
assymetric carbon.Molecules
containingoneormoreof
thesecarboncenters arecon-
sidered chiralmolecules.
Chiral centers can exist in two
forms called enantiomers.
These two forms arenon-
superimposablemirror images
of eachother, but bothhave
similar properties.


