4
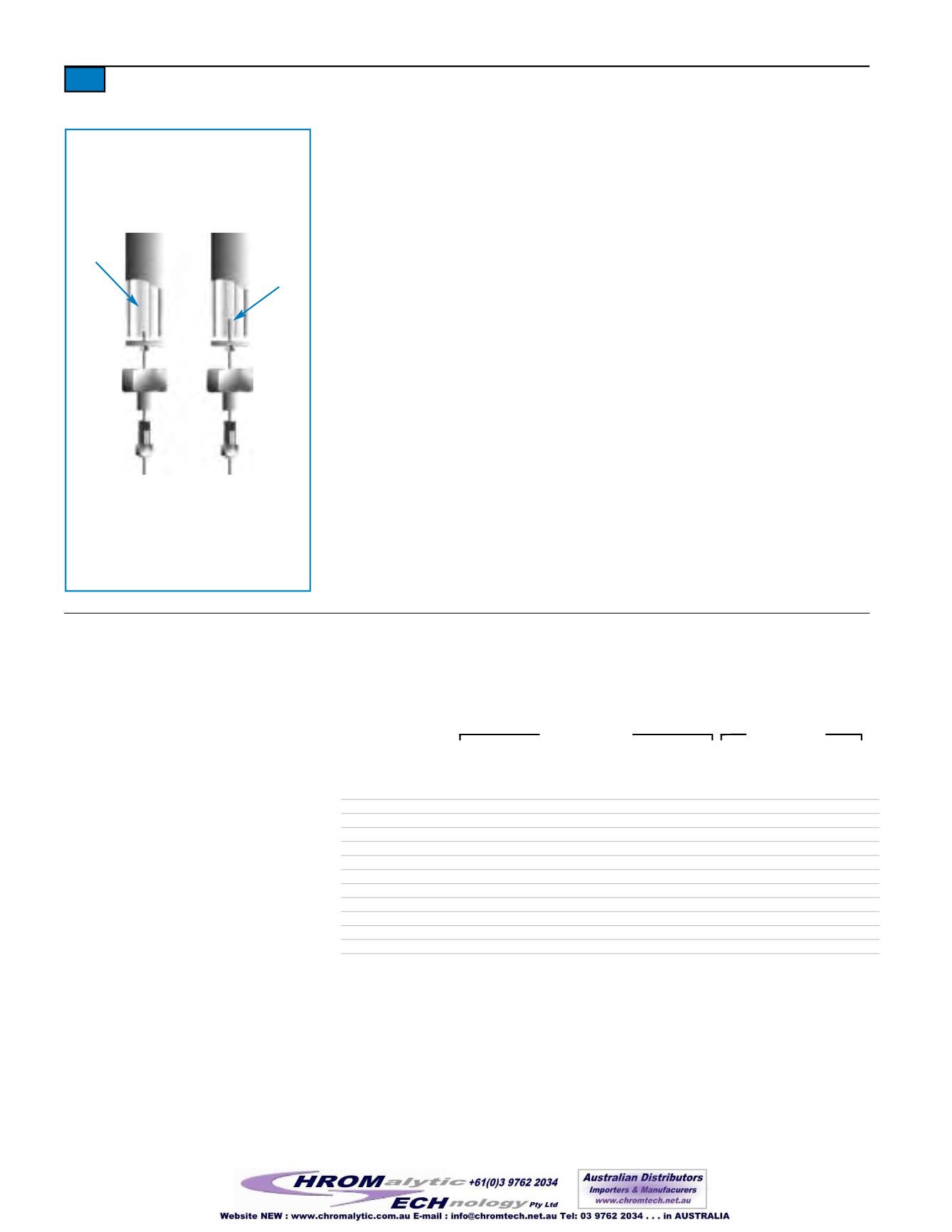
We compared a splitless injection liner and a direct injection liner installed in a capillaryGC
injector (Figure 2). Notice that the splitless injection liner allows the sample vapor to contact
themetal inlet seal at the base of the injection port. Sample vapor potentially can adsorb
onto thismetal surface, or can condense in the area below the column inlet. Either occur-
rence can cause low response for active or highmolecular weight compounds. In contrast,
because the direct injection linermakes a positive seal with the column inlet, all sample
vapor is directed onto the column and cannot interact withmetal injection port surfaces.
Therefore, sensitivity for active and highmolecular weight compounds is significantly
improved.
Table I summarizes the chromatographic results obtainedwhen amixture containing active
and highmolecular weight compoundswas injected into three different splitless injection
liners and two different direct injection liners. Themost typical injection port liner used for
splitless injections is a straight liner with a 4mm internal diameter, packedwith deactivated
fused silica or glasswool (A). The benefit in using a straight liner packedwithwool is that
thewool enhances sample vaporization and thereby improves the responses for highmolecu-
lar weight compounds (represented in this analysis by benzo(b)- and benzo(k)fluoranthene).
However, when the relative responses obtained by using a straight liner packedwithwool
(A) are compared to responses from two splitless injection linerswith a gooseneck restric-
tion of the internal diameter at each end (B andC), it is apparent that the active probes (2, 4-
dinitrophenol, nitrophenol, and pentachlorophenol) were completely adsorbed in the injec-
tion port when the straight liner packedwithwool was used.A double gooseneck liner (B)
improves the response for active compounds by confining the sample cloudwithin the buffer
volume of the liner. This reduces sample contact with themetal support disk in the injector
and, thus, reduces adsorption.A double gooseneck liner with an internal glass spiral (C) not
only provides good response for active compounds, but also provides better vaporization of
high boiling analytes compared to a double gooseneck liner without a glass spiral. Because a
inlet seal
splitless
liner
press-tight
seal
Figure 2.
Splitless and direct injection liners
installed in a splitless capillary injector.
The data illustrate that direct injections improve
responses in general, but especially improve re-
sponses for active high molecular weight com-
pounds compared to splitless injections. A double
gooseneck splitless injection liner provides better
responses than an open, wool-packed splitless in-
jection liner, but it is not until a positive seal is
made between the liner and the capillary column
(D and E) that significant improvements are
observed.
Analystswhousedirect injections insteadof split-
less injections can expect better overall sensitivi-
ty and greater response factors for both active
and highmolecular weight compounds.
30m, 0.32mm ID, 0.25µmXTI-5 column (cat.# 12224),
splitless or direct injection of 1µLXTIMix,
concentration = 29ng/µL.
Oven temp.:
100°C to 285°C@ 6°C/min.,
then to 360°C@ 30°C/min.
(hold 5min.)
Inj./Det. temp.:
250°C/360°C
Carrier gas:
hydrogen
Linear velocity:
40cm/sec. set@ 100°C
FID sensitivity:
8 x 10
-11
AFS
Splitless hold time: 0.75min.
A: splitless injection, 4mm ID injector liner packedwith glasswool (cat.# 20781)
B: splitless injection, double gooseneck injector liner (cat.# 20784)
C: splitless injection, cyclo double gooseneck injector liner (cat.# 20895)
D: direct injection, Uniliner
®
injector liner (cat.# 20335)
E: direct injection, Cyclo-Uniliner
®
injector liner (cat.# 20337)
All analyses conductedwith anAgilent 5890 II GC equippedwith an autosampler
and a dirty inlet seal.
Response Relative to C14
Splitless Injection
Direct Injection
A
B
C
D
E
4mm ID
Double
Cyclo
Analyte
wool-packed Gooseneck Double Gooseneck Uniliner
®
Cyclo-Uniliner
®
benzoic acid
NA
0.90
1.23
1.06
1.21
C14
1.00
1.00
1.00
1.00
1.00
2,4-dinitrophenol
NA
0.33
0.46
0.68
0.58
nitrophenol
NA
0.73
0.93
1.24
1.17
nitroaniline
1.03
0.78
0.93
1.20
1.20
pentachlorophenol
NA
0.45
0.55
0.70
0.66
carbazole
2.01
1.43
1.69
2.17
2.06
C20
1.13
0.89
0.98
1.16
1.09
C21
1.08
0.81
0.92
1.10
1.04
C22
1.13
0.81
0.94
1.15
1.09
benzo(b)fluoranthene
2.18
1.18
1.90
2.22
2.47
benzo(k)fluoranthene
2.09
1.15
1.84
2.27
2.36
Table I.
Responses for active and highmolecular weight compounds are greater with direct
injection, compared to the same injector configured for splitless injection.
splitless injection
liner
Uniliner
®
direct
injection liner
AUniliner
®
direct injection liner prevents
the sample from contactingmetal surfaces
in an injection port, so sample adsorption
and catalytic decomposition are reduced
and responses for highmolecular weight
compounds are greater.
NA –Peak not quantifiable; data not available.


